Iodine has numerous benefits for overall health, but it’s essential to understand the proper dosage and sources to avoid side effects. Good sources of iodine include edible seaweed, eggs, milk, yogurt, and other dairy products.
While iodine promotes thyroid health, excessive amounts can hurt the thyroid gland. It’s crucial to strike a balance and consume iodine in the right amount to reap its benefits without any adverse effects.
1. Introduction To Iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that offers numerous
1.1 What is iodine?
Iodine is an essential mineral that is crucial for maintaining good health. It is a chemical element found in the Earth’s crust and abundant in the ocean. In our bodies, iodine is mainly concentrated in the thyroid gland, which uses it to produce thyroid hormones. These hormones regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development.
Iodine can exist in various forms, such as iodide and iodate, and is commonly found in foods like seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt. It is also available in supplement form for those who have difficulty meeting their iodine requirements through diet alone.
1.2 Importance Of Iodine For Health
Iodine plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some of the critical benefits of iodine:
- Thyroid Function: Iodine is essential for producing thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and support growth and development.
- Brain Development: Adequate iodine levels are crucial for proper brain development, especially during pregnancy and early childhood.
- Healthy Pregnancy: Sufficient iodine intake is essential for pregnant women, as it supports the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system.
- Regulates Metabolism: Thyroid hormones, produced with the help of iodine, play a key role in regulating metabolism, which affects weight management.
- Energy Production: Iodine is needed to efficiently produce and utilize energy, helping to prevent fatigue and keep you energized throughout the day.
- Immune Function: Adequate iodine levels are crucial for a healthy immune system, as they help protect against infections and boost the body’s defense mechanisms.
- Healthy Skin and Hair: Iodine helps maintain the skin’s and hair’s health and integrity, supporting their growth and preventing dryness and brittleness.
- Regulates Body Temperature: Thyroid hormones, regulated by iodine, play a role in maintaining body temperature within a normal range.
- Supports Reproductive Health: Iodine is essential for both male and female reproductive health, contributing to the proper functioning of the reproductive organs.
- Prevents Iodine Deficiency Disorders: Adequate intake of iodine helps prevent iodine deficiency disorders, such as goiter, hypothyroidism, and developmental abnormalities.
- Antioxidant Properties: Iodine exhibits antioxidant properties, helping to protect cells and tissues from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
Iodine is a vital mineral with numerous health benefits, but it’s essential to maintain the right balance. Consuming too much or too little iodine can have adverse effects on health. In the following sections, we’ll explore the proper dosage, sources of iodine, and potential side effects to help you make informed decisions about incorporating iodine into your diet.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/benefits-of-iodine-4570996-5c4550df46e0fb00015f7b71.png)
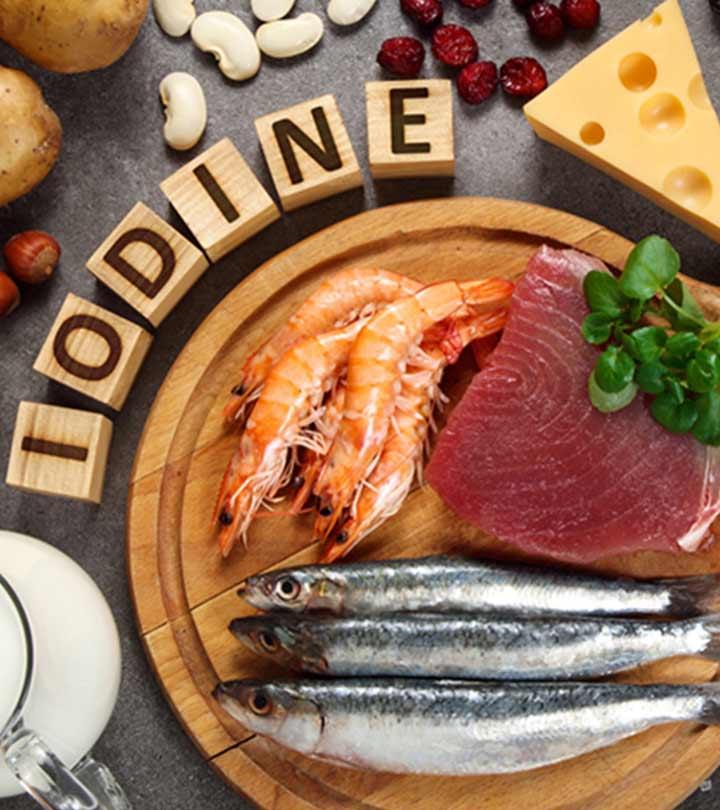
2. Sources Of Iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that helps with average growth and brain development. Good sources of iodine include edible seaweed, eggs, milk, yogurt, and dairy products. However, excessive iodine intake can have adverse effects on the thyroid gland.
Iodine is essential for producing thyroid hormones, which are crucial for average growth and brain development. While iodine deficiency can lead to various health problems, including goiter and intellectual disabilities, getting enough iodine in your diet can offer numerous benefits.
2.1 Natural Food Sources Of Iodine
Natural food sources are an excellent way to meet your iodine needs. Here are some iodine-rich foods you can include in your diet:
- Seafood: Fish, cod, tuna, and shrimp are excellent sources of iodine. Other seafood options, like seaweed and shellfish, are rich in this essential mineral.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are high in calcium and provide a significant amount of iodine.
- Eggs: Including eggs in your diet can contribute to your iodine intake.
- Prunes: Although not as commonly known as seafood or dairy, prunes are also a good source of iodine.
2.2 Iodine-Fortified Foods
In addition to natural sources, many foods are fortified with iodine to help prevent deficiencies. Look for the following iodine-fortified options:
- Iodized Salt: Switching your regular table salt to iodized salt is an easy way to ensure you’re getting enough iodine.
- Fortified Bread and Grains: Check labels for products made with iodized salt or enriched with iodine.
- Fortified Milk Alternatives: Some non-dairy milk alternatives, like soy milk, may be fortified with iodine.
2.3 Iodine Supplements
In some instances, where dietary modifications alone are insufficient, iodine supplements may be prescribed by a healthcare professional. However, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement is essential. They will be able to determine the appropriate dosage and duration.
Remember, while iodine is essential for overall health, excessive intake can lead to adverse effects. It’s crucial to strike a balance and meet your iodine requirements through a healthy and varied diet.
3. Benefits, Dosage, And Side Effects Of Iodine
Iodine offers numerous benefits, including promoting thyroid health and brain development. However, excessive intake can have adverse effects. Understanding the dosage and sources of iodine is essential to avoiding potential side effects.
Iodine is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. It is primarily known for its role in thyroid hormone production, but it also offers a range of other benefits. This section will explore the various health benefits of iodine, the recommended dosage, and potential side effects.
3.1 Health Benefits Of Iodine
Iodine is vital for proper thyroid function as it helps synthesize thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth, and development. Apart from its thyroid-related benefits, iodine also provides several other health advantages:
- Supports Brain Development: Iodine is crucial during pregnancy and early childhood, as it promotes proper brain development and cognitive function.
- Maintains Healthy Metabolism: Adequate iodine levels help regulate the metabolic rate, promoting efficient energy production and weight management.
- Supports Reproductive Health: Iodine is necessary for the production of sex hormones and the proper functioning of the reproductive system.
- Boosts Immune Function: Iodine plays a role in enhancing immune function and protecting against infections and diseases.
- Promotes healthy hair, skin, and nails: Adequate iodine levels contribute to healthy hair, skin, and nails, keeping them strong and vibrant.
- Regulates Blood Sugar Levels: Iodine assists in maintaining stable blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes and related complications.
3.2 Recommended Dosage Of Iodine
The recommended daily intake of iodine varies based on age, sex, and life stage. The following table provides an overview of the recommended daily intake of iodine:
| Life Stage | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 110 mcg |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 130 mcg |
| Children (1–8 years) | 90 mcg |
| Children (9–13 years) | 120 mcg |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 150 mcg |
| Adults (19 years and older) | 150 mcg |
| Pregnant Women | 220 mcg |
| Breastfeeding Women | 290 mcg |
Note: These recommended daily intakes are general guidelines. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on your specific needs.
3.3 Side Effects And Risks Of Iodine
While iodine is essential for overall health, excessive intake can lead to side effects and potential risks. It is crucial to maintain a balanced intake within the recommended dosage. Some common side effects and risks associated with iodine include:
- Iodine Allergy: Some individuals may be allergic to iodine and experience allergic reactions such as skin rashes or swelling.
- Thyroid Disorders: Excessive iodine intake can disrupt thyroid function, leading to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- Stomach Upset: High doses of iodine can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including stomach pain, nausea, and diarrhea.
- Metallic Taste: Excessive iodine intake may result in a metallic taste in the mouth.
- Goiter: Both iodine deficiency and excess can contribute to the development of goiter.
- Interaction with Medications: Iodine supplements may interact with certain medications, including thyroid and blood thinners.
Note: It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting iodine supplements, especially if you have an existing medical condition or are taking medications.
Credit: www.mdpi.com

Credit: www.stylecraze.com
Frequently Asked Questions On 11 Benefits Of Iodine, Dosage, Sources, And Side Effects
What Are The Benefits Of Iodine For Your Health?
Iodine has several benefits for your health, including promoting thyroid function, supporting brain development, and aiding in average growth. It is an essential mineral that your body needs to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and other critical bodily functions.
Where can I find sources of iodine in my diet?
You can find iodine in foods such as iodized table salt, fish, seaweed, eggs, milk, yogurt, and other dairy products. Including these foods can help you get enough iodine to meet your body’s needs.
Can Iodine Be Harmful If Consumed In Excessive Amounts?
Although iodine is essential for your health, consuming excessive amounts can have adverse effects. Too much iodine can cause a metallic taste, soreness in teeth and gums, a burning sensation in the mouth and throat, stomach upset, and other side effects.
It’s important to consume iodine in moderation.
Conclusion
Iodine provides numerous benefits for overall health, particularly in thyroid function and brain development. Maintaining a balanced intake of iodine is essential to avoid both deficiency and excessive consumption, as they can lead to health problems. Good sources of iodine include iodized table salt, fish, and seaweed.
It is essential to be aware of potential side effects and consult a healthcare professional before taking iodine supplements. Incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet can promote optimal health and well-being.

