Iodine has numerous benefits for your health, but it’s important to be aware of the proper dosage, sources, and possible side effects. Some of the benefits of iodine include promoting thyroid health, supporting normal growth, and aiding in brain development.
It is essential to consume enough iodine through your diet, as a deficiency can lead to health problems. However, excessive amounts of iodine can have a negative impact on your thyroid gland. Good sources of iodine include iodized salt, fish, and seaweed.
It’s crucial to maintain a balanced intake of iodine to ensure optimal health without any adverse effects.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/benefits-of-iodine-4570996-5c4550df46e0fb00015f7b71.png)
Introduction To Iodine
Iodine offers numerous benefits, including promoting thyroid health and brain development. However, excessive intake can have negative effects. It is important to find the right balance and ensure sufficient iodine intake without going overboard.
What is iodine?
Iodine is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of our bodies. It is a trace element, meaning we need it in small amounts for optimal health. Our bodies do not produce iodine naturally, so it is important to obtain it through our diet or supplements. Iodine is mainly stored in the thyroid gland, which uses it to produce thyroid hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Why is iodine important for health?
Iodine is vital for our overall health and well-being. Here are some key reasons why iodine is important:
- Thyroid Health: Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, which are crucial for regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
- Brain Development: Adequate iodine intake during pregnancy and early childhood is crucial for proper brain development in infants and young children.
- Energy Levels: Iodine helps convert food into energy, allowing us to stay active and energized throughout the day.
- Immune System Function: Iodine plays a role in supporting the immune system and protecting against infections.
- Regulates Hormones: Iodine helps regulate the balance of various hormones in the body, promoting overall hormonal health.
- Supports Fetal Development: Adequate iodine levels during pregnancy are crucial for the healthy development of the fetus.
As you can see, iodine is involved in various essential processes within our bodies, making it crucial for overall health and well-being.
Recommended Dosage Of Iodine
The recommended daily intake of iodine varies depending on age, gender, and life stage. Here are the general recommended daily allowances (RDAs) for iodine:
| Life Stage | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 110 mcg |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 130 mcg |
| Children (1–8 years) | 90-120 mcg |
| Children (9–13 years) | 120 mcg |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 150 mcg |
| Adults (19 years and older) | 150 mcg |
| Pregnant women | 220 mcg |
| Breastfeeding women | 290 mcg |
It is important to note that certain individuals, such as those with thyroid disorders or pregnant women, may require higher iodine intake under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Now that we understand the importance of iodine and how much we need, let’s explore the various sources of iodine in our diet and the potential side effects of iodine supplementation.
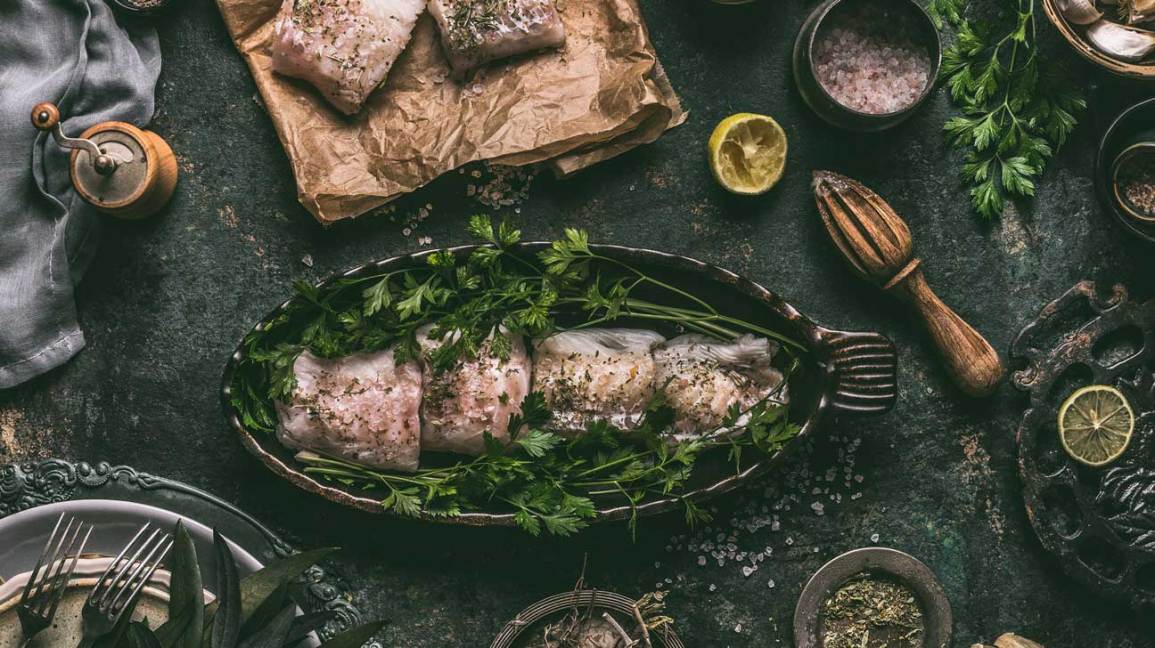
Sources Of Iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that helps with thyroid health and normal growth. Good sources include iodized table salt, fish, and seaweed. However, excessive intake can lead to negative effects on the thyroid gland.
Iodine-rich Foods
When it comes to obtaining iodine naturally, incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet is a great way to go. These foods contain significant amounts of iodine, ensuring that your body receives the essential mineral it needs. Some iodine-rich foods include:
- Edible seaweed
- Eggs
- Milk
- Yogurt
- Dairy products
- Prunes
Eating a variety of these foods can help you maintain optimal iodine levels and support thyroid health. So, why not try incorporating some seaweed into your diet or enjoying a glass of milk or yogurt daily?
Iodized Salt
One of the most common and accessible sources of iodine is iodized salt. This type of salt is fortified with iodine, ensuring that your meals are seasoned with a healthy dose of this essential mineral. Using iodized salt in your cooking and at the table can provide you with a consistent supply of iodine.
However, it’s important to note that while iodized salt can be a convenient source of iodine, it’s not the only one you should rely on. Incorporating a variety of iodine-rich foods into your diet is still necessary to ensure adequate intake.
Supplements
In addition to natural food sources and iodized salt, supplements can also be a reliable way to boost your iodine levels. Iodine supplements come in various forms, such as tablets or liquid drops, and can be easily incorporated into your daily routine.
If you’re considering taking iodine supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs. They can assess your current iodine levels and provide guidance on the right supplement to support your overall health.
Remember, while supplements can be beneficial, they should never replace a healthy diet rich in iodine-containing foods. Supplements should always be used as a complement to a well-rounded eating plan.
Whether you choose to incorporate iodine-rich foods, use iodized salt, or take supplements, it’s essential to be mindful of your iodine intake. Striking the right balance will ensure that you reap the many benefits of this vital mineral without experiencing any undesirable side effects.
Potential Side Effects And Risks Of Iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining thyroid health and overall well-being. While it provides numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of its potential side effects and risks. In this section, we will discuss the possible side effects of excessive iodine intake, iodine deficiency symptoms, and interactions with other medications.
Possible Side Effects Of Excessive Iodine Intake
Consuming too much iodine can lead to various side effects, which include:
- Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism: Excessive iodine intake can overstimulate the thyroid gland, causing symptoms like rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and weight loss.
- Metallic taste and soreness: Some people may experience a metallic taste in their mouth or soreness in their teeth and gums after consuming too much iodine.
- Burning sensation: In rare cases, excessive iodine can cause a burning sensation in the mouth and throat.
- Stomach upset: Digestive issues like stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting may occur when iodine intake exceeds the recommended levels.
- Thyroid dysfunction: While iodine is essential for thyroid function, excessive intake can disrupt the delicate balance, leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
It is crucial to maintain a balanced iodine intake to avoid these potential side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms after consuming iodine supplements or high-iodine foods, consult a healthcare professional.
Iodine Deficiency Symptoms
Iodine deficiency can also have negative effects on your body. Some common signs of iodine deficiency include the following:
- Goiter: a visible enlargement of the thyroid gland, resulting in a swollen or lumpy neck.
- Hypothyroidism: Insufficient iodine intake can lead to an underactive thyroid, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
- Cognitive impairments: Inadequate iodine levels can impair brain development and cognitive function, particularly in infants and children.
- Decreased fertility: Iodine deficiency may affect reproductive health, leading to difficulties in conceiving.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect iodine deficiency, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Interactions With Other Medications
It is important to consider potential interactions between iodine supplements, iodine-rich foods, and certain medications. Some medications that may interact with iodine include:
| Antithyroid drugs | Iodine supplements may interfere with the effectiveness of antithyroid medications used to treat hyperthyroidism. |
| Lithium | Iodine supplements may decrease the effectiveness of lithium, a medication commonly used for bipolar disorder. |
These are just some examples of potential interactions. Always inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking to ensure safe and effective use.
While iodine offers numerous health benefits, it is essential to maintain a balanced intake to avoid potential side effects and risks. If you have any concerns or questions about iodine supplementation or your iodine status, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.

Frequently Asked Questions On 11 Benefits Of Iodine, Dosage, Sources, And Side Effects
Q: What Are The Benefits Of Iodine?
A: Iodine provides various benefits, including supporting thyroid health, promoting normal growth, aiding brain development, and assisting in the production of thyroid hormones.
Q: What Are The Sources Of Iodine?
A: Good sources of iodine include iodized table salt, seafood (especially fish), seaweed, dairy products, eggs, and some fruits like prunes.
Q: Can Iodine Be Harmful?
A: While iodine is essential for health, taking too much iodine can have negative effects on the thyroid gland. It is important to consume iodine in moderation and avoid excessive intake.
Conclusion
Iodine offers numerous benefits for overall health, particularly in supporting thyroid function and brain development. It is important to ensure that you are getting enough iodine through your diet and avoiding excessive intake, as it can have negative effects on the thyroid gland.
Good sources of iodine include foods like edible seaweed, eggs, milk, yogurt, and dairy products. Be mindful of potential side effects and consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.

